

What is IVF
Test-tube baby is the common name of in vitro fertilization - embryo transfer technology, refers to the use of artificial methods to make egg cells and sperm in vitro fertilization, and early embryonic development, and then transplanted into the mother's womb development and birth of the baby.
Originally developed in collaboration with British obstetrician Patrick Steptoe and physiologist Robert Edwards, the technique has become a worldwide scientific sensation.
On July 25, 1978, the world's first test-tube baby was born in Britain.
In December 2011, a wealthy businessman in Guangzhou gave birth to octuplets through IVF.
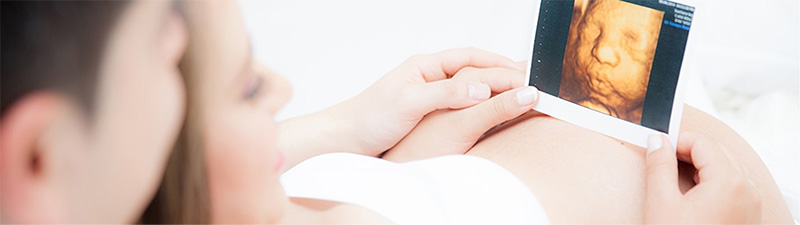
A "test-tube baby" is not an actual baby grown in a test tube. Instead, several eggs are taken from an ovary and combined with the man's sperm in a laboratory to form an embryo. The embryo is then transferred to the uterus, where it is implanted in the mother's uterus and conceived. Normal conception requires sperm and egg to meet in the fallopian tube, where the two combine to form a fertilized egg, which then returns to the uterine cavity to continue the pregnancy.
"Test tube baby" can be simply understood as a laboratory test tube instead of the function of the fallopian tubes and called "test tube baby". Although IVF was originally used to treat infertility caused by blocked fallopian tubes, it has been found to help patients due to endometriosis, infertility caused by abnormal sperm count or shape, or even unexplained infertility.

First generation test-tube technology
The first generation of test-tube baby is also called routine test-tube baby, namely IVF - ET.
The first generation of test-tube baby technology is mainly for female infertility research out of assisted fertility technology!
In 1978, British experts steptoe and E. dowrds customized the world's first test-tube baby, known as a miracle in the history of human medicine. It involves placing sperm and eggs outside the body and using various techniques to fertilize the eggs, incubate them for a few days and then transfer them to the uterus to impregnate the woman and give birth.
Second generation test tube technology
The second generation of test-tube baby technology, also known as oocyte intracytoplasmic single sperm injection (ICSI), is a microfertilization technology developed on the basis of in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer (IVF-ET), which directly injects sperm into oocyte cytoplasm to achieve the purpose of pregnancy assistance
In 1992, Dr. Palermo and Dr. Liu Jia-en from Belgium successfully applied ICSI in human body for the first time, which greatly improved the success rate of IVF technology. ICSI not only increased the success rate, but also greatly expanded the indications of IVF technology for male and female infertility.

What is the third generation of test-tube technology The third generation of test-tube babies, also known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), refers to the method of taking genetic material of embryos for analysis before embryo transfer in IVF-ET, diagnosing whether there are abnormalities, screening healthy embryos for transfer, and preventing the transmission of genetic diseases. The detection substance was taken from one cell of 4-8 cell stage embryo or the first bipolar of ovum before and after fertilization. The sampling did not affect embryonic development. Detection by single-cell DNA analysis, one is polymerase chain reaction (PCR), detection of male and female sex and single gene genetic disease; The other is fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), which tests for sex and chromosomal diseases. Edwards came up with the idea of PGD back in 1964. |
|

Japanese IVF process
domestic
Domestic consultation: understand your needs, answer relevant questions
Physical examination report: Both the male and female shall have physical examination in a domestic third-class hospital
Protocol confirmation: Initial confirmation of IVF protocol can be made within 3-5 working days after receipt of medical examination report
Domestic signing: domestic signing service agreement
Go to Japan
Itinerary arrangement
Japan
Make an appointment with a doctor
Test tube cycle: 10-12 days after insertion of the stimulation needle embryo culture for 5-6 days
Embryo transfer: After the promotion of excretion, the menstrual cycle begins after the second day of menstruation. It is expected that the embryo can be transferred after 3 weeks of medication
Successful pregnancy test
Return to China
After the test tube is finished, return home to await the birth
Physical examination item list (male) 01 Blood Routine (CBC) Blood Type 02 (BIGR) 03 Positive and Negative Blood Type (RhGr) Hemoglobin (Hemoglobin typing) 05 Anti HIV 06 Syphilis Serum Test (VDRL) 07 Hepatitis B Antigen (HBsAG) 08 Hepatitis B Core Antigen (HBcAb) Sperm Analysis -- Sperm Quality (Sprm Analysis) | Physical examination item list (female) Regular item 01 Blood routine (CBC). Blood Type 02 (BIGR) 03 Positive and Negative Blood Type (RhGr) Hemoglobin (Hemoglobin typing) 05 Anti HIV 06 Syphilis Serum Test (VDRL) 07 Hepatitis B Antigen (HBsAG) 08 Hepatitis C Antigen (Anti-HCv) 09 German Measles Virus Antibody (Rubella LGG) 10 The Thyroed Function test Get tested the day after your period 01 sex hormone six items Follicle-producing hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Estradiol (E2) Progesterone (P) Testosterone (T) Prolactin (PRL) Size and number of basal follicles detected (vaginal ultrasound) Triple AMH test -- To assess egg reserve in the ovaries (anti-Camus hormone) 4. Between the 10th and 14th days of menstruation: Check endometrial thickness (guided ultrasound) |
 Japan physical examination
Japan physical examination
 Medical treatment in Japan
Medical treatment in Japan
 Regenerative Medicine - Stem cells
Regenerative Medicine - Stem cells
 Comprehensive information
Comprehensive information
